
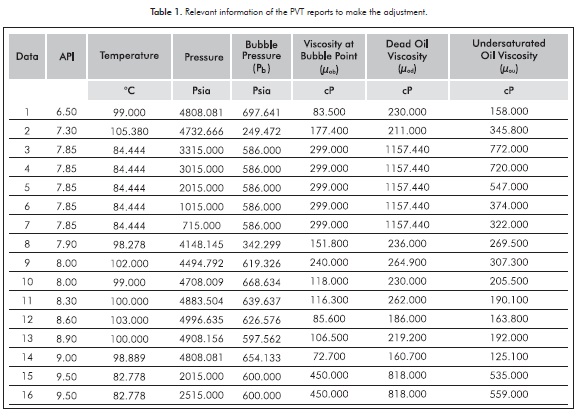
The laboratory method for calculating the bubble-point pressure, p b, of a crude oil was discussed earlier in the context of the differential liberation test. MW o is the molecular weight of the crude oil, lb/lb-moleīubble-Point Pressure of the Crude Oil, p bĪs already discussed, the bubble-point pressure is the pressure that first bubble of gas evolves from an undersaturated crude oil during pressure reduction.It is the properties of the separated phases that we are most interested in, as these are more representative of the processes occurring in the reservoir. In addition, due to the density differences between oil and gas phases, gravity will also act to separate the two phases. Consequently, as gas evolves from the oil, this difference in the viscosity allows the gas to move faster than the oil and to separate from the source oil from which it evolved. What is the differential liberation test trying to model? In the reservoir, as gas comes out of solution, it typically has a much lower viscosity than the oil phase.

The pressure, liquid volume, and gas volume are then used in the calculation of the appropriate properties for black oils. This process is then repeated until the desired final pressure is reached (Step 8). The gas is then expelled from the piston under isobaric (constant pressure) conditions by reducing the piston volume and allowing the gas to escape through a valve in the system (Step 5). At this point, the pressure and the oil and gas volumes in the cell are measured.
Cp to cst viscosity converter free#
Up until the bubble-point pressure is reached, all measurements have been single-phase (liquid hydrocarbon) measurements.Īfter the bubble-point pressure has been reached, the volume is increased further until a significant volume of free gas has developed (Step 4). This pressure is the bubble-point pressure of the crude oil. This process is continued for several pressure steps until the first bubble of gas (red) is observed through a window in the cell (Step 3). At Step 2, the pressure in the cell will be less that the original pressure due to the expansion of the crude oil. The volume of the cell is then increased by extending the piston outward (Step 2), and the pressure and volume are recorded.
In a differential liberation test, a crude oil sample (green) is introduced into the cell at the initial reservoir pressure and temperature (Step 1 in Figure 3.07).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
